Understanding CT Scans for Lung Cancer Detection
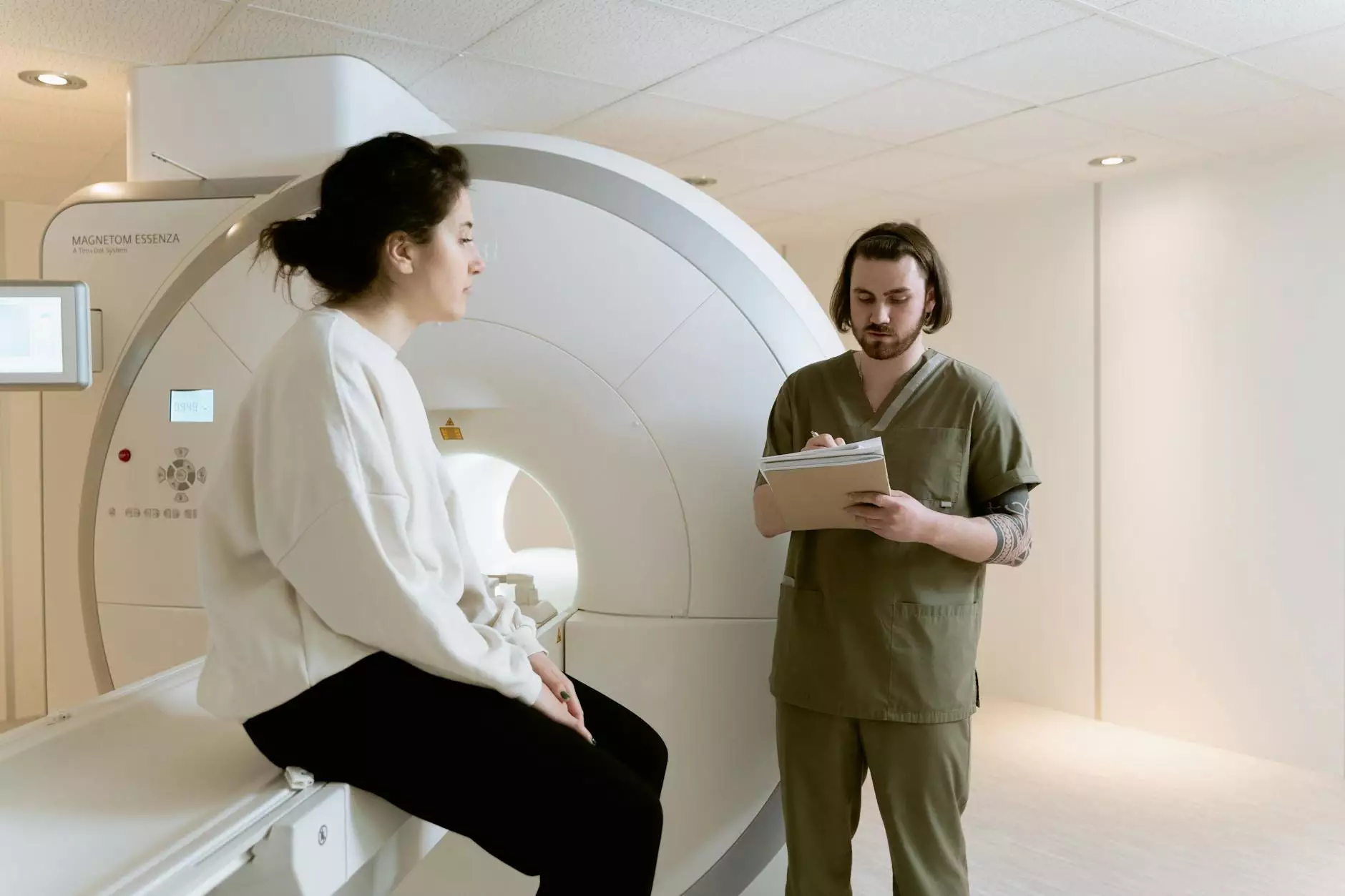

Lung cancer remains one of the most significant health issues worldwide. With early detection being crucial for effective treatment and improved survival rates, CT scans have emerged as vital tools in this endeavor. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about CT scans for lung cancer, including how they work, their benefits, and what to expect during the procedure.
What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan is a sophisticated imaging technique that generates detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It utilizes a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce high-resolution images, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize structures within the body with remarkable clarity.
How CT Scans Work
The process involves the patient lying on a table that slides into a large circular machine. This machine rotates around the body, taking multiple X-ray images from different angles. A computer then processes these images to create a comprehensive view of the internal structures, including the lungs.
The Importance of CT Scans for Lung Cancer
In the realm of lung cancer detection, CT scans have become indispensable. They play a crucial role in:
- Early Detection: CT scans can identify lung nodules or tumors at an earlier stage than traditional X-rays, which is essential for improving prognosis.
- Staging Cancer: They help in determining the extent of the cancer, assessing lymph node involvement, and identifying metastasis.
- Guiding Treatment Decisions: Detailed imaging assists oncologists in devising tailored treatment plans based on the size and location of the tumors.
Who Should Get a CT Scan for Lung Cancer?
CT scans for lung cancer screening are typically recommended for:
- Individuals aged 50 to 80 years with a history of heavy smoking.
- People with a significant smoking history who have quit within the last 15 years.
- Those with a family history of lung cancer or other risk factors, such as exposure to radon or asbestos.
It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate personal risk factors and determine if a CT scan is necessary.
Benefits of CT Scans for Lung Cancer Detection
The advantages of utilizing CT scans for lung cancer detection are manifold:
- High Sensitivity: CT scans are more sensitive than other imaging methods, allowing for the detection of smaller tumors.
- Non-invasive Procedure: The CT scan process is non-surgical and typically takes only a few minutes to complete.
- Enhanced Treatment Planning: Detailed images enable physicians to strategize more effective treatment approaches.
- Monitoring Response to Treatment: CT scans can be used to assess how well the cancer is responding to treatment over time.
What to Expect During a CT Scan
Before undergoing a CT scan for lung cancer, patients should be aware of what to expect:
Preparation
Preparing for a CT scan typically includes:
- Informing your doctor about any allergies, particularly to contrast materials used in some scans.
- Avoiding certain foods or drinks prior to the scan if instructed; NPO (nothing by mouth) might be required for a few hours.
- Wearing comfortable clothing and possibly a gown provided by the medical facility.
The Scanning Procedure
During the CT scan:
- You will be positioned on the examination table, which will move through the CT scanner.
- It’s essential to remain still and hold your breath for short intervals while the scan is being conducted.
- If contrast dye is used, you might receive it through an intravenous (IV) line, which could cause a brief warming sensation.
Post-Procedure and Results
After the scan, you can typically resume normal activities unless instructed otherwise by your healthcare provider. The results will usually be analyzed by a radiologist, and you can expect to discuss the findings with your doctor within a few days.
Risks and Considerations
While CT scans provide critical information, they do carry some risks:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to radiation, although the benefits often outweigh the risks.
- False Positives: Occasionally, CT scans may detect abnormalities that turn out to be non-cancerous, leading to unnecessary anxiety and additional testing.
Discuss these risks with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Alternatives to CT Scans
While CT scans are highly effective, there are alternative imaging techniques for lung cancer detection:
- X-rays: These are less detailed than CT scans but may still be useful in certain situations.
- MRI Scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses magnetic fields and does not involve radiation but is less commonly used for lung cancer.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): PET scans can provide metabolic information about lung nodules, helping to distinguish between benign and malignant growths.
Advancements in CT Technology
The field of imaging technology is rapidly evolving, and recent advancements have improved the precision and efficacy of CT scans:
- Low-Dose CT Scans: These scans reduce radiation exposure while still achieving high-resolution images.
- 3D Imaging: Innovative techniques allow for three-dimensional reconstruction of images, providing a comprehensive view for better diagnosis.
Conclusion
In summary, CT scans for lung cancer play a critical role in early detection and treatment planning. If you or someone you know is at risk for lung cancer, a CT scan could be a life-saving procedure. Always discuss with your healthcare provider to understand the benefits and risks associated with this imaging method.
With a commitment to health and wellness, Hello Physio encourages proactive healthcare measures, including regular screenings and effective physical therapy options to support recovery and overall well-being.